Nexus
Runtime Implementation
Provides the routing and publishing infrastructure for cross-network AI orchestration
The Breakthrough
Voluntary Dynamic Loops
Agents self-organize into coordination loops based on capability, not configuration. No hardcoded workflows—just voluntary contribution.
Global Recursive AI
Loops spawn sub-loops infinitely. Each layer aggregates intelligence from the layer below. Collective intelligence emerges naturally.
New Intelligence
Not just routing messages—creating new insights through multi-agent collaboration. The whole becomes greater than the sum of its parts.
Cross-Network Orchestration
Agents across different networks, organizations, and trust boundaries coordinate seamlessly through policy-driven routing.
Decentralized Consensus
No central authority decides. Agents vote, merge, and reach consensus through configurable aggregation strategies.
Full Audit Trail
Every decision, every contribution, every loop execution is logged. Complete transparency and accountability at every level.
Nexus Console
Manage your realm hierarchy, configure policies, and monitor agent activity through the Nexus Console interface.
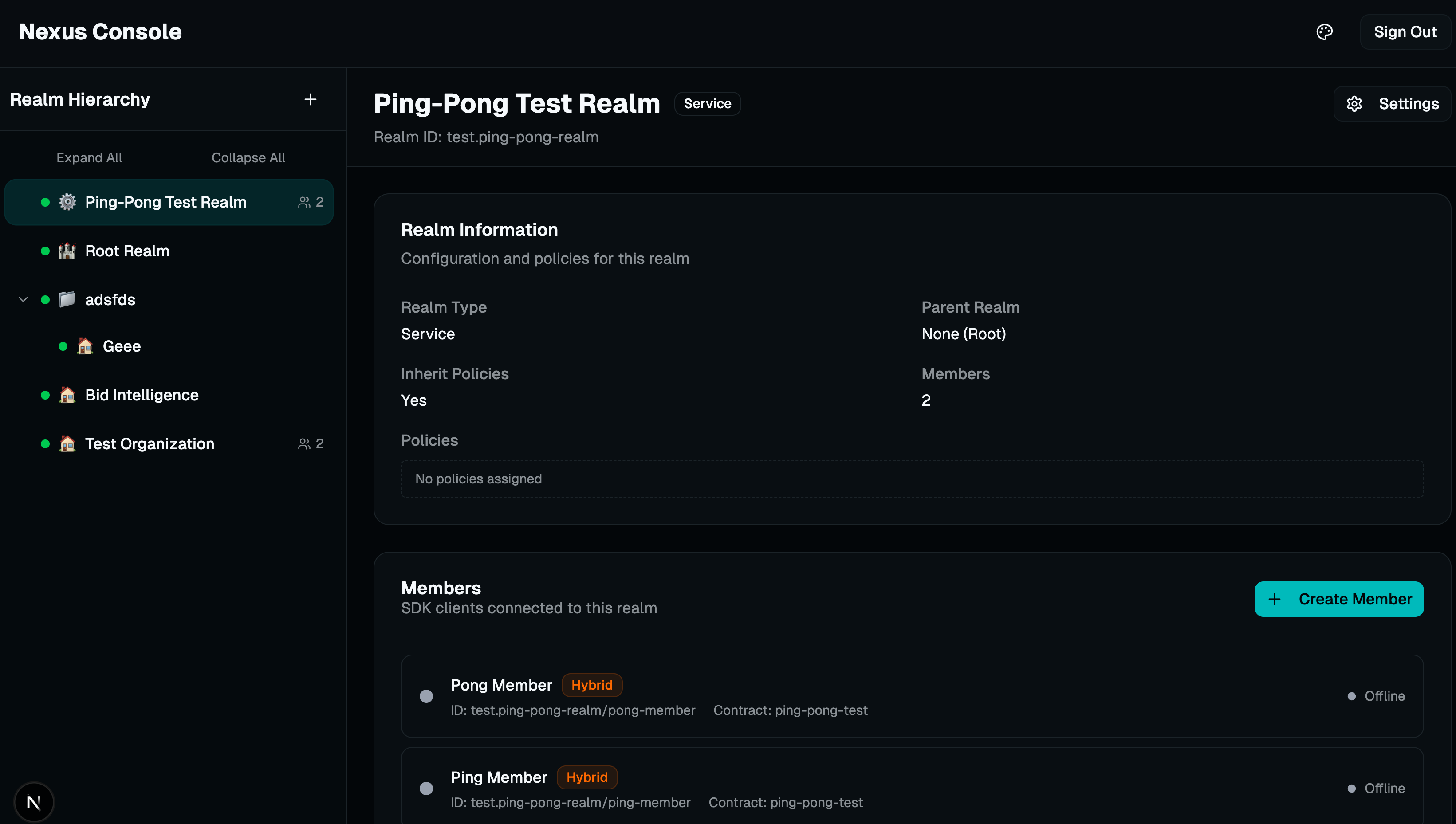
Realm Hierarchy
Visualize and manage your nested realm structure with expandable tree navigation
Policy Management
Configure routing policies, inheritance rules, and access controls per realm
Member Monitoring
Track SDK clients, connection status, and agent activity in real-time
How Nexus Works
Agents Connect to Realms
SDK clients connect to Nexus and join specific realms based on their role (service, event, loop participant). Each realm acts as a security boundary with its own policies.
Routing & Publishing
Nexus routes service calls, publishes events, and broadcasts loop invitations across the network. Policy engines determine which agents can communicate based on capabilities and trust boundaries.
Loop Coordination
When a loop is initiated, Nexus broadcasts to all capable agents. Agents self-select to participate, execute in parallel, and Nexus aggregates results using the configured strategy (vote, merge, consensus).
Recursive Intelligence
Loops can spawn sub-loops, creating recursive coordination patterns. Each level aggregates intelligence from below, enabling emergent collective intelligence that scales infinitely.
See It In Action
The Nexus MVP demonstrates agents routing through realms in real-time. Watch as the Ping-Pong test agents coordinate through the runtime.
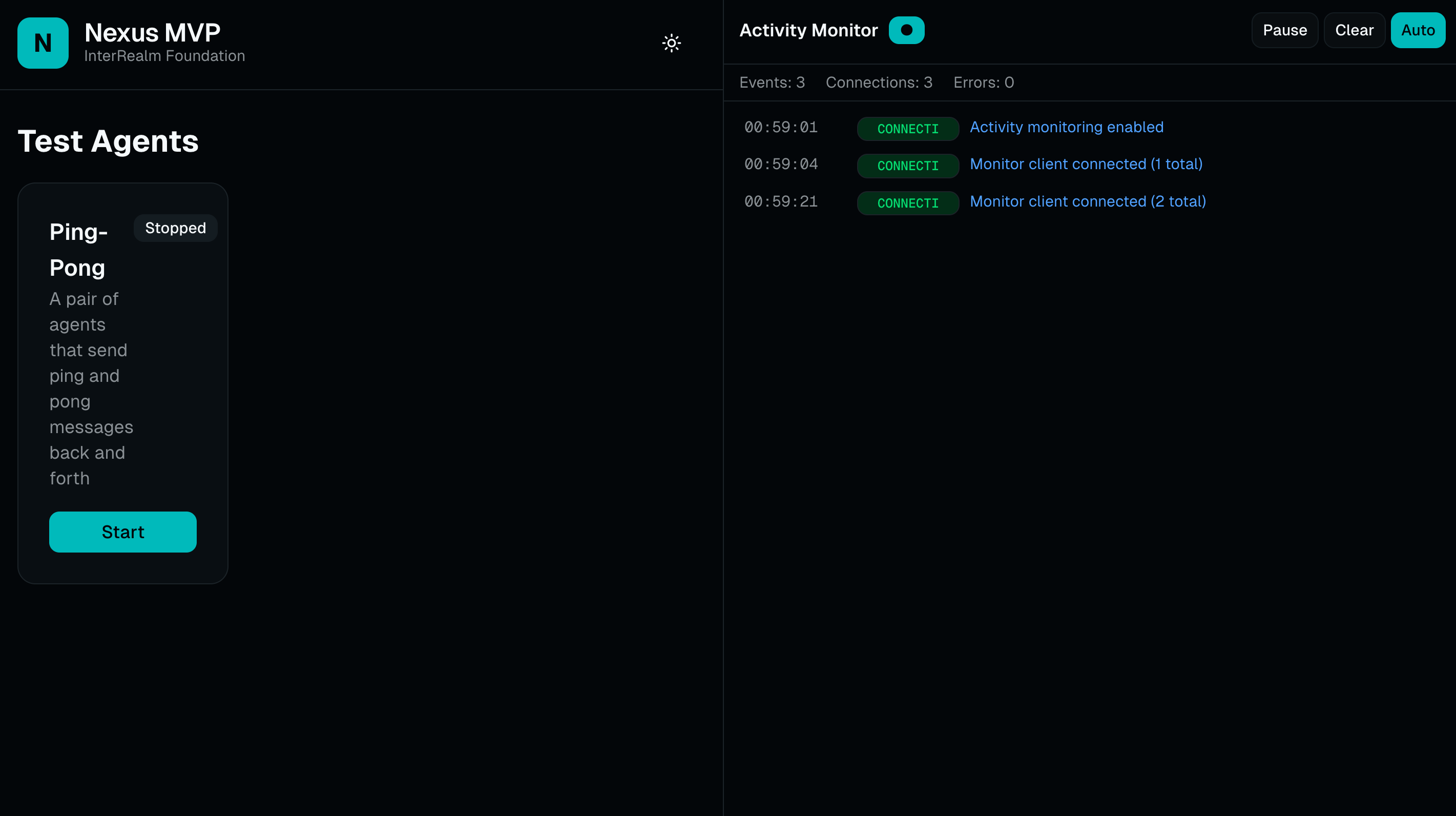
Live Agent Coordination
Test agents send ping and pong messages back and forth, demonstrating real-time routing through Nexus realms with full activity monitoring.
Activity Monitoring
Track connections, events, and errors in real-time. Every agent interaction is logged with timestamps and connection status.
Realm-Based Routing
Realms are the foundational building blocks of InterRealm. Each realm acts as a security boundary and routing domain, defining what agents have access to and how they coordinate.
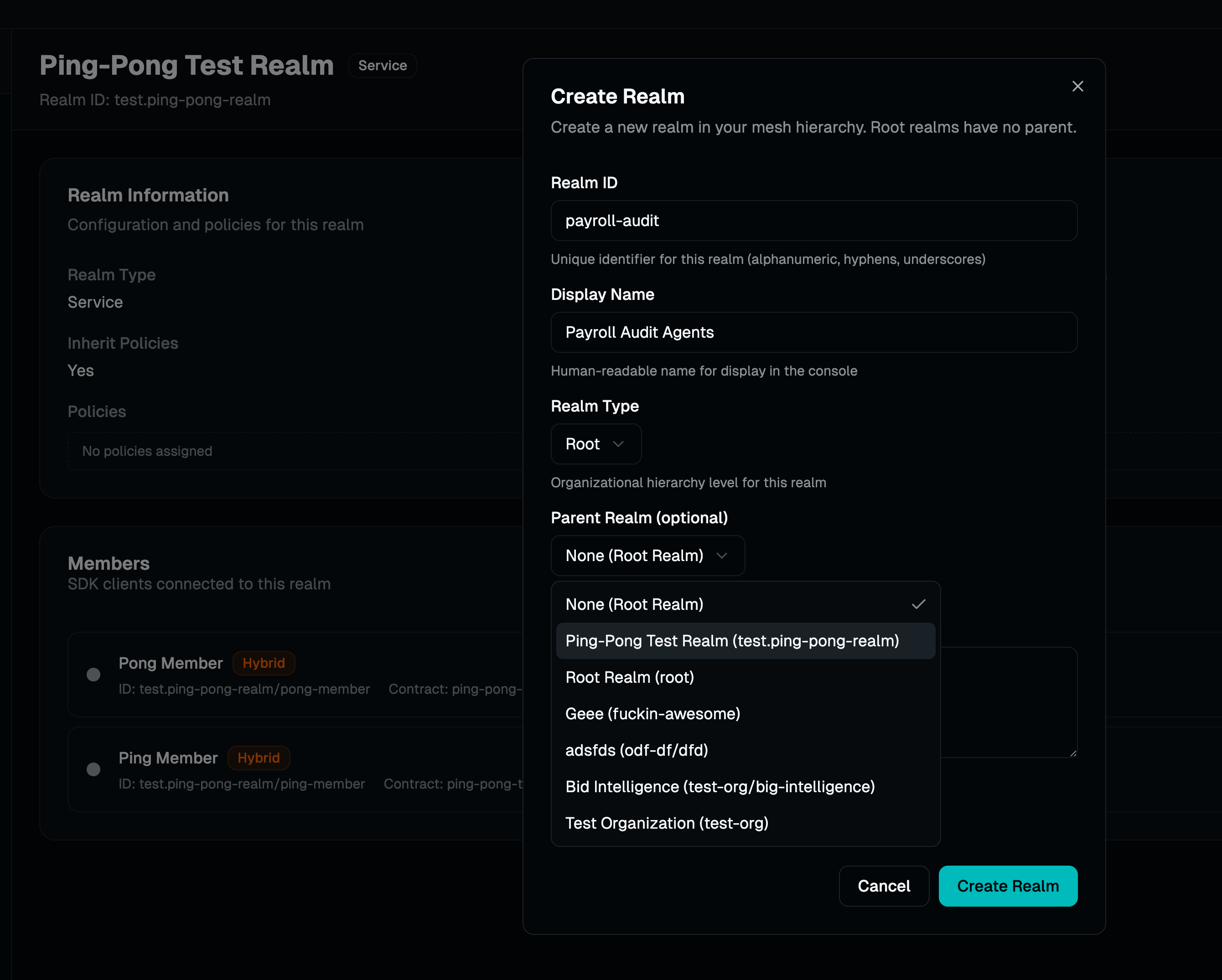
Hierarchical Organization
Realms form a parent-child hierarchy. Each realm can contain AI agents, logical resources, or other nested realms. Routing flows through this hierarchy based on policies.
- •Root realms have no parent and define top-level boundaries
- •Child realms inherit policies from parents (configurable)
- •Routing decisions respect the hierarchy and trust boundaries
Dynamic Access Control
Members (SDK clients) connect to realms and gain access based on realm policies. No explicit dependency injection—agents discover and coordinate dynamically.
- •Agents declare capabilities, not dependencies
- •Cross-realm loops enable internet-scale coordination
- •Policy-driven routing determines who can communicate
The Protocol Schema
Realms are defined using the InterRealm protocol schema. Each realm specifies its type (Root, Service, Organization), parent relationship, and member access rules. This schema enables:
Realm Hierarchy
Nested realms create organizational structure and routing paths
Member Management
SDK clients connect and agents coordinate within realm boundaries
Policy Enforcement
Define what agents can access and how they interact across realms
Connecting Systems to InterRealm
Members are connection points for external systems using the InterRealm SDK. They define how agents, services, and logical resources participate in the mesh with delegated security and dynamic routing.

SDK Connection Slots
Members act as slots for external systems to connect via the InterRealm SDK. Each member has a type (Consumer, Provider, or Hybrid) and optional contract specification.
- •Consumer members call services and subscribe to events
- •Provider members expose services and publish events
- •Hybrid members do both—full participation in the mesh
Delegated Security Model
Members inherit security context from their realm. Routing and access control are defined at the realm level, not hardcoded in agent logic.
- •Agents don't manage credentials—realms do
- •Policy changes propagate without code changes
- •Cross-realm coordination respects trust boundaries
Injected Without Awareness
This is where the magic happens. Agents declare what they can do (capabilities), not what they need (dependencies). Nexus handles routing, discovery, and coordination dynamically:
Dynamic Discovery
Agents find each other through capability matching, not explicit configuration
Cross-Internet Loops
Coordination spans networks and organizations through realm-based routing
Zero Configuration
Add new agents without updating existing ones—they discover each other automatically
Secure API Key Management
After creating a member, Nexus generates a unique API key for SDK authentication. This key is shown only once and must be stored securely by the client application.
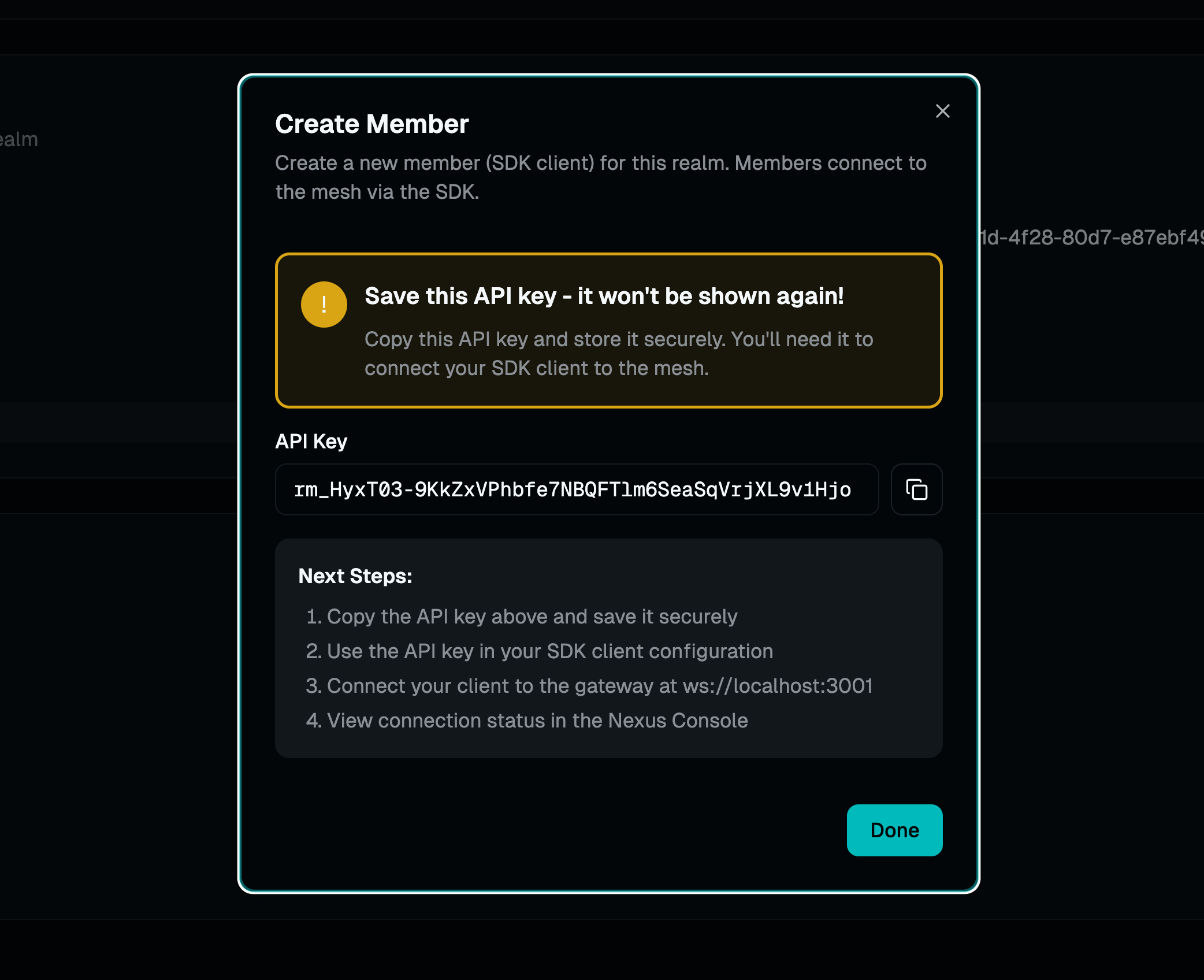
One-Time Display
API keys are generated once and never stored in plain text. After creation, the key is displayed only once—if lost, a new member must be created.
- •Keys are cryptographically secure random strings
- •Nexus stores only hashed versions for verification
- •Copy and save immediately—it won't be shown again
SDK Configuration
Use the API key in your SDK client configuration to authenticate and connect to the Nexus gateway. The SDK handles all authentication and connection management.
- •Pass the API key to the SDK client constructor
- •Connect to the gateway WebSocket endpoint
- •Monitor connection status in the Nexus Console
Security Best Practices
API keys are the only credential needed to connect to InterRealm. Treat them like passwords and follow these security guidelines:
Store Securely
Use environment variables or secret management systems—never commit keys to source control
Rotate Regularly
Create new members periodically and deactivate old ones to minimize exposure risk
Limit Scope
Create separate members for different services to isolate access and simplify revocation
Monitor Usage
Track connection activity in the Nexus Console to detect unauthorized access attempts
Ready to Build with Nexus?
Explore the InterRealm Stack and start building distributed AI systems